How chocolate is made
From bean to bar. Until the finished chocolate bar arrives at your home, it takes time and requires a few steps. The manufacturing process of premium chocolate is not complicated, but a real challenge.
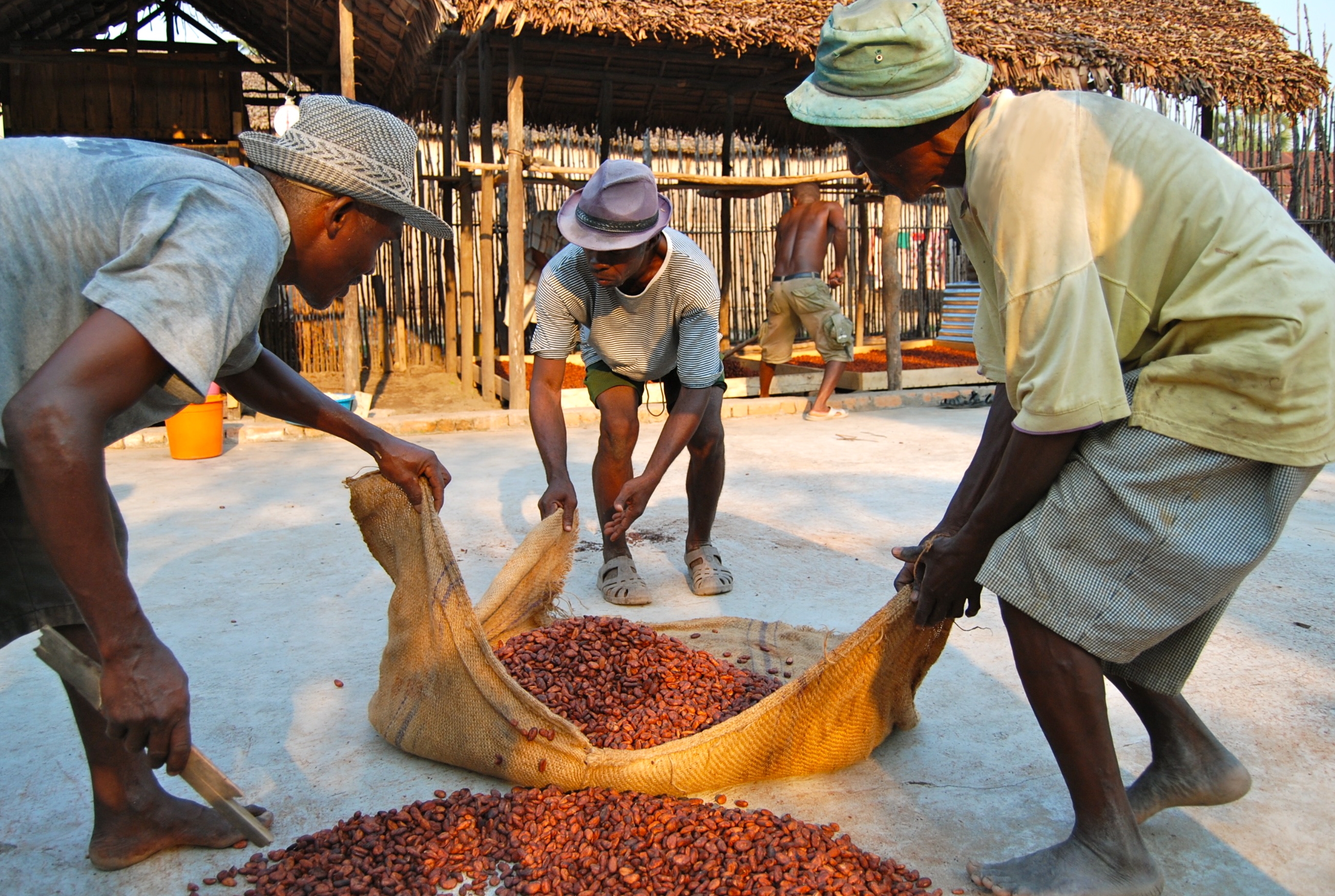







Harvesting
Using long knives the cocoa fruit is separated from the trees. It must be taken with extreme care in order not to injure the seed pillow, from which the fruit has emerged. Otherwise at these points no further fruit could grow any more. The fruits are then opened with machetes and brought out the pulp, as well as the cocoa beans from the shells .
Fermentation
The fermentation in large wooden boxes is particularly prevalent today. This method is used by most of the larger farms and farming cooperatives. The fermentation in barrels and wooden boxes has the advantage that the cocoa beans are not easily attacked by pests. So the beans are usually for about five to six days in wooden boxes. The exact fermentation time varies , depending on the cocoa variety , 2-6 days. During this time, a fermentation process, the fermentation proceeds. This high temperatures of approximately 46°C to 52°C. caused Triggered by those temperatures run from a variety of chemical and biological processes . On the first day the pulp becomes liquid and then evaporates , the more the temperature rises . It is crucial for the subsequent chocolate, the beans sprout briefly , then die off by the high temperatures and the high acidity . Without the germination of the beans , the chocolate would not have their desired taste. The killing of germination is necessary to make the beans tough. With the death of the beans , the cell walls are destroyed and the cell sap can spread throughout the bean. This is one reason that the bitter taste of the beans is mitigated and precursors of the later flavors emerge. In addition, the previously whitish- yellow beans get their brown color . To ensure that there is no faulty fermentation , the cocoa beans are vaccinated on some plantations at the beginning of fermentation with a starter microflora . Otherwise, one has to rely on the transfer the bacteria for example by flying. The inoculum is obtained from the current production and fermented juices enriched with various yeasts. To improve the quality of the beans may be sorted prior to fermentation also on their size . How to reach a uniform fermentation even with different sized cocoa beans.
Drying of the cocoa bean
After fermentation, the beans contain up to 55 % water. In order to be storable and thus suitable for further processing , they must be dried . For this they are spread out on mats and exposed to two weeks of the tropical sun. During drying is reduced , the weight of the beans to more than 50% and the water content is reduced to a maximum of 6 %. Thereby, the durability of the beans is significantly improved. By sunlight , the aroma of the beans is also developed.
Transport
The cocoa beans are processed normally not in the producing countries , but in Europe and North America. The transport takes place by sea. For this purpose, the cocoa beans are packed in 60kg jute bags .
Cleaning
As the cocoa beans arrive in the chocolate factory, they are often contaminated with foreign bodies such as dust, sand, wood , glass, stone , metal and jute fibers. These foreign bodies will removed with the aid of sieves, magnets and air currents.
Roasting
The usual cocoa bean roasting temperatures are between 100 ° C and 140 ° C. The exact temperatures depend on the chocolate type and quality ( for example, the bean size ) and on the desired flavor. Also plays a role in whether to be produced from the beans of cocoa powder or chocolate. Usually beans are for the production of cocoa powder used at higher temperatures than roasted beans for chocolate production . Fine cocoas also be roasted at lower temperatures. So be fine cocoa for chocolate production in the lower temperature range from 100 ° C to 115 ° C geröstet.Die roasting time depends on the cocoa beans, the roasting temperature and roasting of the employed. Short roasting times at high temperatures are from 15 to 20 minutes. Longer roasting processes at low temperatures can take over an hour.
Since you can only bad at the same roasting cocoa beans of different sizes due to the different lengths of roasting time many companies to go on no longer the whole beans to roasting but the cocoa nibs (called Nibs).
During roasting, the beans continue to lose moisture, and run it from chemical processes, which are essential for the taste and aroma of chocolate. Roasting can also take place after breaking and peeling. After roasting , the cocoa beans have to be cooled quickly in order to prevent over-roasting. The aim of roasting : Full open up the flavor, and it caused up to 400 flavors.
Breaking & peeling
During this process the beans are first broken by strong rolls into small pieces. Then the light shell parts are blown away by a strong stream of air remains the cacao nibs. The breaking can also be done by a union breaker. In that the beans being thrown at high speed against steel plates and so broken. The advantage of this method is also the beans of different sizes are broken properly.
Cocoa nibs finishing
In the cocoa nibs have some undesirable flavor and odor substances are present (such as acetaldehyde , acetone, i-butanol , ethanol, i -propanol, ethyl acetate, i -pentanal , methanol, diacetyl ). These substances are eliminated at the end of the chocolate-making through the conching. Starting from the fact that the unwanted substances can be easily unsubscribe from the solid cocoa nibs, as from the cocoa mass , in which the elements are encapsulated by the cocoa butter, you have already started the cocoa nibs to decorate. This allows the time and energy consuming conching be shortened. The processing is done in a special pressure reactor. If you want to make cocoa powder so the cocoa nibs in this reactor, an alkali solution is added. In the production of chocolate are added a solution of sugar , malt, salt and other substances. Benefits of cocoa nibs Performance : The time for the conching ( Endveredlung ) can be greatly shortened. The flavor of the chocolate can be enhanced. Molds and yeasts, and microorganisms are destroyed mostly.
Grinding
The nibs are ground. Here, the cellular tissue of the fragments is torn and exposed the cocoa butter. The generated heat will melt the cocoa butter comes out of the pores and coats the fragments. The cocoa nibs is for liquid cocoa mass. The cocoa mass already has a certain resemblance to the later end product and is ready for making chocolate or cocoa powder. For grinding different mills may be used, for example ball mills or roller systems.
Mixing the ingredients
First, the cocoa mass is mixed with the respective ingredients. Depending on the recipe, different amounts of cocoa butter, sugar, milk powder and other ingredients. Stirring is carried out in a slightly oversized blender. The mixing of the ingredients can take up to 30 minutes, but the time strongly depends on the ingredients used. Then had become of the various liquid and solid ingredients a solid, kneadable and fine-grained mass. The chocolate mass has now almost the flavor of the finished chocolate, you tried it, one clearly a little "gritty" sensation on the tongue, because the individual grains are still too large.
Refining
Thus chocolate gets soft as possible consistency and one on the tongue has no "sandy" feeling more, the cocoa mass is rolled into a refiner by several rolling into a wafer-thin layer. The limit up to which the human tongue can warnehmen individual grains is about 30 thousandths of a millimeter, but varies greatly from person to person.
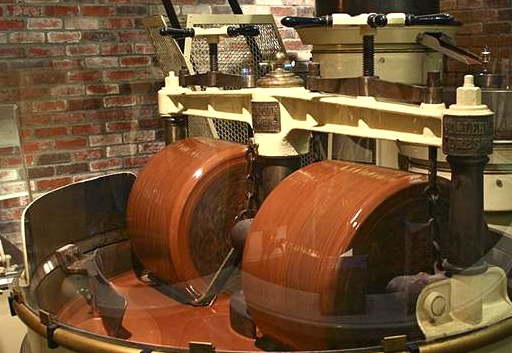
Conching
During conching, the chocolate is stirred in the conche and heated up to 90 ° C. Through the hours of heating and stirring the fat flows back out of the column and is evenly distributed around the particles, so the result is a delicate liquid mass. By oxygen, and heat of the material is also withdrawn from moisture so that the moisture content is now less than 1%.
During conching it comes to a redistribution within the mass. Flavors from the fat dissolve and be absorbed by particles. The result is a flavor of sugar surfaces and the flavor is considerably more harmonious.
In addition, through the conching undesirable odor and taste substances discharged (including acetaldehyde , acetone , i- butanol , ethanol , i- Prpanol , ethyl acetate , acetic acid, i- pentanal , methanol, diacetyl ). If required by the chocolate recipe is added towards the end of conching again cocoa butter.
Tempering and pre-crystallization
After the chocolate mixture has left the Conche, she has a temperature of about 50 ° C and is too thin for further processing. Man "seeded" the mass now with some fat crystals and leaves the chocolate then slowly after a certain temperature curve at about 27 ° C to cool. By "seeding" and the slow cooling, the formation of fat bloom is prevented , which occurs when the cocoa butter crystallized upon cooling. Although the does not affect the taste, the white spots that may arise here , but do not look very appetizing. Through the process of tempering the chocolate its silky sheen and matt fraction , the "cracking" sound during breaking of the tablets.
Filling and cooling
Finally, the chocolate is poured into molds panel. Once the chocolate has obtain the appropriate form, it is cooled and packaged.